Boy, girl or polyhydramnios - we study the shape of the abdomen in expectant mothers. Pregnant woman belly shape
The problem of "acute abdomen" during pregnancy is one of the complex borderline obstetric-surgical problems. Its reasons are shown in Table. 37. During pregnancy, the enlarged uterus displaces the abdominal organs, which disrupts their function and causes an atypical clinical course of many acute diseases. In addition, an obstetrician well versed in physiological changes during pregnancy and obstetric complications may not be able to diagnose acute surgical disease; on the contrary, the surgeon often takes the symptoms he has discovered for manifestations of pregnancy. These factors often lead to diagnostic errors and, consequently, to a potentially dangerous delay in the active surgical treatment of acute surgical disease.
Surgical interventions, except for cesarean section, are performed in 0.2-2.2% of all pregnancies.
The problem of "acute abdomen"
Table 37
Surgical causes of "acute abdomen" during pregnancy
Diagnosis of diseases of the abdominal cavity
A thorough history taking is very important for the diagnosis of surgical pathology during pregnancy. It is also important to know exactly the gestational age (the second trimester of pregnancy is the safest for surgical intervention).
Patients with an "acute abdomen" are shown a thorough examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist to exclude obstetric and gynecological pathology. The number of abdominal examinations should be as small as possible to establish a diagnosis, so as not to provoke an increase in uterine tone.
Early and accurate diagnosis of abdominal diseases in pregnant women is complicated by the following factors:
Altered anatomical relationships;
Difficulty palpation of the abdominal organs;
Erased clinical symptoms;
Symptoms similar to the usual discomfort of pregnancy;
Difficulties in differential diagnosis of surgical and obstetric pathology.
Pain
Pain is the main symptom of an "acute abdomen" during pregnancy. According to the localization of pain, the cause of the "acute abdomen" can be assumed. Generalized pain is sometimes due to peritonitis due to bleeding, inflammatory exudation, or the presence of intestinal contents in the abdomen. Pain, localized in the lower abdomen centrally, is often associated with an increase in the tone of the uterus, in the lateral lower abdomen - with torsion, rupture of the capsule of the neoplasm (cyst or tumor) of the ovary. descending pathology or
sigmoid colon with localization of pain in the lower left quadrant of the abdomen is rare due to the relatively young age of the patients. Pain in the middle abdomen in early pregnancy may be associated with the intestines, pain in the upper sections - with the pathology of the liver, spleen, gallbladder, stomach, duodenum or pancreas.
Other symptoms
After the first trimester of pregnancy, abdominal pain, combined with nausea and vomiting, is usually caused by pathology of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
A common symptom of acute surgical pathology during pregnancy is diarrhea (with the exception of cases of nonspecific ulcerative colitis).
Loss of consciousness with pain and symptoms of peritoneal irritation may indicate acute surgical abdominal disease with organ rupture and bleeding. A temperature above 38 °C indicates an infection, the localization of which is specified by other clinical symptoms.
Laboratory diagnostics
The results of laboratory tests used to diagnose surgical disease during pregnancy are evaluated differently than usual. An increase in the level of leukocytes over 12,500 in any trimester of pregnancy, as well as a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, is of diagnostic value.
Fetal risk
Potential risk to the fetus must be minimized - risk due to maternal disease (Fig. 107), anesthesia, drug exposure, diagnostic x-ray exposure, and surgery.
Currently, anesthesia is fairly safe during pregnancy, but may increase the incidence of spontaneous abortions, especially in the first trimester.
The use of analgesics in the postoperative period as a whole does not give pronounced side effects. Aspirin should only be used for a short time, avoid long-term use or high doses. In pregnant women, it is permissible to use antibiotics of three
groups - cephalosporins, penicillins, macrolides, sulfonamides and aminoglycosides are not recommended, tetracyclines are categorically contraindicated.
 Rice. 107. Risk of pregnancy complications in acute abdominal diseases
Rice. 107. Risk of pregnancy complications in acute abdominal diseases
X-ray irradiation is carried out for pregnant women only if the risk of undiagnosed surgical pathology exceeds the risk of irradiation of the fetus (mainly it is a suspicion of intestinal obstruction).
Fetal hypoxia is the main danger for him during surgical intervention in the mother. Therefore, in the preoperative period, during the operation and in the postoperative period, it is necessary to monitor the p0 2 of the mother, the oxygen saturation of her blood. Be sure to prevent compression of the inferior vena cava in the supine position. Better oxygenation of the fetus is also facilitated by oxygen therapy and replenishment of the BCC, a drop in maternal blood pressure can directly lead to fetal hypoxia. A pronounced decrease in uteroplacental blood flow due to direct vasoconstriction and an increase in uterine tone is observed with the use of vasopressor drugs, especially drugs with α -adrenergic activity, so they should be avoided. For the diagnosis of fetal hypoxia during surgical interventions in late pregnancy, CTG monitoring and dopplerometry are indicated before surgery and in the postoperative period.
The severity of the inflammatory process due to surgical disease affects the outcome of pregnancy to a greater extent than the surgical intervention itself. The frequency of preterm birth increases with severe surgical complications, especially with peritonitis.
Principles of surgical interventions
In the "acute abdomen" clinic, immediate surgical intervention is indicated, the delay in diagnosis and operation is the main factor leading to an increase in maternal complications and perinatal losses.
If the operation is not urgent and can be delayed, it is better to postpone surgery until the second trimester or postpartum period.
In subacute situations, the decision to operate should be made cautiously.
Preoperative preparation includes adequate hydration, the presence of blood products and appropriate premedication that does not reduce maternal and fetal blood oxygenation.
Adequate anesthesia must be provided.
Maternal hypotension should be prevented (avoid supine position).
Avoid unnecessary manipulation of the pregnant uterus.
In the absence of obstetric indications for a caesarean section, a caesarean section should not be performed along with surgery.
Postoperative care depends on the duration of pregnancy and the operation performed. At the end of pregnancy, careful monitoring of the fetal heart rate, preferably CTG with simultaneous recording of the fetal heart rate and uterine tone, allows timely diagnosis of fetal hypoxia and the threat of preterm birth. Excessive use of sedatives, overhydration should be avoided and electrolyte disturbances should be corrected in a timely manner.
Appendicitis
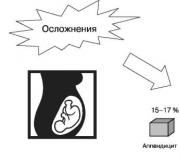
Acute appendicitis is the most common surgical pathology during pregnancy (Fig. 108). Its frequency is 0.4-1.4 per 1000
changes. The frequency of appendectomy is on average 1 per 1000 pregnancies, the diagnosis of appendicitis, according to foreign data, is confirmed intraoperatively in 65%, i.e. about 1 in 1500 pregnancies, which dictates the need for a thorough revision of the abdominal cavity when an unchanged appendix is found.

Rice. 108. The frequency of acute appendicitis depending on the gestational age
Destructive forms are observed during pregnancy 2-3 times more often than in non-pregnant women, which is associated with late diagnosis and surgery. Maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality are much higher if appendicitis is complicated by peritonitis.
Clinical symptoms
Pregnancy makes it difficult to diagnose appendicitis for the following reasons.
1. Anorexia, nausea, vomiting are regarded as signs of pregnancy, not appendicitis.
2. The appendix rises upward as the gestational age increases, which leads to a change in the localization of the pain syndrome.
3. Moderate leukocytosis is always noted in normal pregnancy.
Particularly difficult is the differential diagnosis of acute appendicitis with diseases such as acute pyelonephritis, renal colic, placental abruption, malnutrition of the myomatous node.
A pregnant woman, especially in late pregnancy, may not have symptoms that are considered "typical" of non-pregnant women. There is almost always pain in the right lower or middle quadrant of the abdomen, but during pregnancy it is sometimes regarded as a round ligament sprain or urinary tract infection. During pregnancy, the appendix moves upward and outward. After the first trimester of pregnancy, the process is significantly displaced from the McBurney point with horizontal rotation of its base. This rotation continues until the 8th month of pregnancy, when more than 90% of the appendixes are located above the iliac crest and 80% are rotated anteriorly to the right hypochondrium. An important role is played by the tendency to constipation during pregnancy, which causes stagnation of the intestinal contents and an increase in the virulence of the intestinal flora, as well as hormonal changes leading to a functional restructuring of the lymphoid tissue.
The most constant clinical symptom in pregnant women with appendicitis is pain in the right abdomen, although the pain is often localized atypically. Muscle tension and symptoms of peritoneal irritation are less pronounced, the longer the gestational age. Nausea, vomiting, anorexia - as in non-pregnant women. At the beginning of the disease, the temperature and pulse rate are relatively normal. High fever is not typical for the disease; in 25% of pregnant women with appendicitis, the temperature is normal. To establish the diagnosis, diagnostic laparoscopy is indicated, especially in early pregnancy.
Due to the atypical clinical picture, the time from the onset of the disease to surgical treatment in almost 80% of patients exceeds 12 hours, and in every fourth - more than a day (Fig. 109), which contributes to an increase in the frequency of complicated forms of acute appendicitis.
As the gestational age increases, the caecum and appendix are located high, the formation of adhesions and the restriction of infection by the greater omentum become unlikely, as a result of which the frequency of destructive forms (Fig. 110) and diffuse purulent peritonitis increases.
Clinical analysis of case histories of pregnant women with acute appendicitis, conducted by the staff of the department, showed a high incidence of destructive forms of acute appendicitis in pregnant women.
All pregnant women with acute appendicitis complain of abdominal pain, and all have local soreness. Nausea and vomiting in
I trimester do not have great diagnostic value, as often these are manifestations of early toxicosis of pregnancy. In the II and III trimesters, as a rule, there are no manifestations of toxicosis, and these symptoms become more important in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis, occurring respectively: nausea - in almost 70%, vomiting - in about 50% of cases. Loose stools may appear in 20% of patients. Tension of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall and symptoms of peritoneal irritation are noted mainly in the first trimester (up to 75%), and after

Rice. 109. Time from disease onset to appendectomy in pregnant women
 Rice. 110. The frequency of occurrence of various forms of acute appendicitis depending on the duration of pregnancy
Rice. 110. The frequency of occurrence of various forms of acute appendicitis depending on the duration of pregnancy
and the uterus from the small pelvis in the II trimester - in 30-50%, in the III trimester - only in 28% of patients. In the diagnosis of acute appendicitis, the symptoms of Rovsing and Sitkovsky are of great importance, especially in the second half of pregnancy. Quite often, one can see an increase in pain when the uterus is displaced towards the localization of the appendix (Brando's symptom). Temperature reaction occurs only in half of the patients, as well as leukocytosis of more than 12,000. But almost all patients have tachycardia up to 100 beats per minute (Table 38).
Table 38
Clinical symptoms of acute appendicitis in pregnant women depending on the duration of pregnancy
Symptoms of acute appendicitis | Trimester |
||
Stomach ache | |||
Local pain on palpation | |||
loose stool | |||
Muscle tension | |||
Symptoms: | |||
Shchetkin-Blumberg; | |||
Rovsing; | |||
Sitkovsky; | |||
Temperature >37 °С | |||
Leukocytosis >12000 | |||
Tachycardia >80 | |||
Laboratory signs
The diagnosis is mainly established clinically. Relative leukocytosis of pregnancy (normal up to 12,500) makes it difficult to diagnose the infection. In 75%, there is a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left. In the analysis of urine, there may be pyuria (in 20%) and microhematuria due to the transition of the inflammatory process to paraurethral tissue.
ku, a close connection between the appendix and the ureter (usually with a retrocecal location of the process), which sometimes makes it difficult to differentiate between appendicitis and pyelonephritis.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following pathologies:
Rupture of the cyst of the corpus luteum;
Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor;
Ectopic pregnancy;
Placental abruption;
premature birth;
Sprain of round ligaments;
chorioamnionitis;
Malnutrition of the myomatous node;
salpingitis;
Pyelonephritis;
Cholangitis;
mesenteric adenitis;
Neoplasms;
diverticulitis;
Meckel's diverticulum.
Treatment
There is a statement that "death from appendicitis is death from delay" (Fig. 111). Treatment of uncomplicated appendicitis during pregnancy is appendectomy.
Anesthesia
Epidural anesthesia is the optimal method of pain relief. In some cases, if artificial ventilation is necessary, endotracheal anesthesia is used. Estimated technical difficulties during appendectomy, the patient's fear of surgery should incline the surgeon to the choice of general anesthesia.
Online access
As an operative access with an undoubted diagnosis in the first trimester of pregnancy, the Volkovich-Dyakonov access is used. In the II and III trimesters, this access is not always sufficient, therefore, they use
 Rice. 111. Surgical treatment of appendicitis
Rice. 111. Surgical treatment of appendicitis
Xia its modification according to the principle - the longer the gestational age, the higher the incision. The last weeks of pregnancy, the incision is made slightly above the ilium due to a significant displacement of the caecum and appendix upwards. In case of doubt in the diagnosis and diffuse peritonitis, a lower median laparotomy is indicated. Currently, many authors recommend performing a lower median laparotomy, which provides the possibility of a thorough revision of the abdominal organs, given that the correctness of the preoperative diagnosis of acute appendicitis in pregnant women is 60-80%. It is possible to use laparoscopy only up to 16-17 weeks of pregnancy.
Active therapeutic tactics in relation to pregnant women allows you to complete the operation by suturing the abdominal cavity tightly. If drainage is necessary, drains are removed transabdominally, microirrigators can be brought to the dome of the caecum for subsequent administration of antibiotics into the abdominal cavity. In destructive forms, peritonitis, abscess formation, intravenous antibiotics are indicated.
Impact on pregnancy outcome
Appendicitis increases the chance of miscarriage or premature birth, especially with peritonitis.
Causes of the threat of termination of pregnancy in the development of acute appendicitis 15%.
Infection of the uterus by contact - along the peritoneum, through the fimbrial end of the fallopian tubes.
Purulent metastases from the appendix to the placenta, membranes, to the wall of the uterus.
The action of the alpha-phospholipase system of some bacteria, the specific activity of which is much higher than the activity of the phospholipase of the chorion, amnion, decidua.
Increased intrauterine pressure.
Reflex transmission of irritation from the peritoneum of the process to the peritoneum covering the uterus.
The formation of adhesions that contribute to premature uterine contractions.
In order to prevent premature termination of pregnancy, generally accepted measures are taken - bed rest, antispasmodics, tocolysis with magnesium sulfate, vitamin E. Tocolytic therapy is not needed for uncomplicated appendicitis, but in severe forms it is usually required (tocolysis with magnesium sulfate). If labor activity develops at the end of the third trimester shortly after the operation, then it should not be slowed down.
Undiagnosed appendicitis often leads to the development of labor. A large uterus often contributes to the local delimitation of infection, however, after delivery, when the uterus decreases sharply, pus enters the abdominal cavity. In such cases, the picture of "acute abdomen" develops sharply a few hours after birth. In other cases, when appendicitis begins to develop already in the postpartum period, it usually rarely leads to peritonitis.
Forecast
Maternal mortality is minimal, perinatal losses are associated with preterm birth or diffuse peritonitis and sepsis, i.e. with the severity of appendicitis, and not with surgery. Reproductive losses - about 15%, the frequency of abortion is higher if surgery is performed after 23 weeks (reproductive losses 22%).
Peritonitis with appendicitis
Mortality in diffuse peritonitis, according to various authors, is 23-55% for the mother, 40-92% for the fetus, the highest mortality is in the third trimester of pregnancy. This is due to a number of reasons, among which the main place is occupied by a decrease in the plastic properties of the peritoneum during pregnancy, pushing up the omentum and other peritoneal formations, the presence of a huge full-blooded suction surface of the uterus, as a result of which intoxication is more violent than outside pregnancy.
Unfavorable results of treatment (Fig. 112) of diffuse purulent peritonitis in pregnant women are primarily caused by a decrease in immunity characteristic of pregnancy, an increase in the absorption of toxins due to an increase in the surface of the pregnant uterus, increased blood supply to the pelvic organs, upward displacement of the greater omentum, a decrease in its antibacterial activity and other changes in the body of a pregnant woman, leading to a deterioration in antimicrobial protection. In this regard, for the relief of diffuse purulent peritonitis, in addition to removing the appendix and sanitizing the abdominal cavity, as a rule, termination of pregnancy is indicated. Treatment algorithm in the first trimester: after the lower median incision - instrumental emptying of the uterus through the vagina, appendectomy, sanitation
 Rice. 112. Treatment of peritonitis
Rice. 112. Treatment of peritonitis
abdominal cavity. In case of late caesarean section under conditions of a purulent process, it is recommended to extirpate the uterus with fallopian tubes, sanitize and drain the abdominal cavity. An attempt to maintain pregnancy after appendectomy and sanitation of the abdominal cavity can contribute to the appearance of inter-intestinal abscesses, the development of a septic condition and death, as well as the preservation of an infected uterus during cesarean section.
Cholecystitis and cholelithiasis
Gallbladder disease is the second most common surgical pathology during pregnancy (1-6 per 10 thousand pregnancies). At least 3.5% of pregnant women have gallstones. The frequency of acute cholecystitis requiring surgical intervention during pregnancy ranges from 1 in 6.5 thousand to 1 in 25 thousand pregnancies.
Risk factors for developing gallbladder disease in pregnant women:
Parity;
History of taking oral contraceptives (doubling the risk of gallbladder disease);
Increased lithogenic properties of bile;
Changes in the motility of the biliary tract, stasis of bile;
In the II and III trimesters - an increase in the volume of the gallbladder by almost two times, a decrease in its ability to empty.
Clinical signs
Same as in non-pregnant women, but anatomical changes associated with pregnancy make diagnosis difficult:
Anorexia;
Nausea, vomiting;
Subfebrile condition;
Pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen.
The liver and diaphragm are located higher, the gallbladder is higher than the right costal arch, and the appendix can also be located in the right upper quadrant. Cholecystitis is often accompanied by pain in the epigastrium, the right subscapular region, and even in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen or the left lower one. Attacks of pain - usually after eating, last from several minutes to several hours. Nausea, vomiting, fever, muscle tension in the right upper quadrant are possible. The gallbladder in pregnant women is usually inaccessible to palpation.
Laboratory signs:
Leukocytosis with a shift to the left;
It is possible to increase the concentration of liver enzymes (AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase), bilirubin, although relatively normal levels of ACT, ALT and a slightly elevated alkaline phosphatase (in pregnant women it is increased due to the synthesis of alkaline phosphatase by the placenta) and bilirubin are more typical.
Ultrasound: gallstones (absent in 10%), changes in the bladder wall.
Differential Diagnosis:
Appendicitis;
pancreatitis;
Preeclampsia.
Treatment
Initially, conservative treatment of cholecystitis (Fig. 113) is recommended during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, because surgical intervention at this time may be accompanied by a miscarriage. Surgical treatment is indicated for pregnant women with severe clinical symptoms, repeated hospitalizations and concomitant pancreatitis, then the prognosis for the further development of pregnancy is usually favorable. In recent years, laparoscopic cholecystectomy has been considered the treatment of choice for most patients. The optimal time for surgical intervention for cholecystitis (Fig. 114) is the II trimester.
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis ranks third in frequency among acute surgical pathologies in pregnant women. Its frequency is from 1:3 thousand to 1:12 thousand pregnancies, however, maternal mortality is high - 3.4%, perinatal mortality is 11%, which indicates the importance of timely diagnosis of this disease.
The cause of pancreatitis is the presence of activated digestive enzymes in the pancreas. Most often (as in non-pregnant women) pancreatitis is caused by cholelithiasis.
 Rice. 113. Conservative treatment of cholecystitis
Rice. 113. Conservative treatment of cholecystitis
 Rice. 114. Surgical treatment of cholecystitis
Rice. 114. Surgical treatment of cholecystitis
Etiological factors of acute pancreatitis:
Cholelithiasis;
Hypertriglyceridemia (for example, a hereditary defect in lipoprotein lipase);
The impact of drugs (tetracyclines, thiazide diuretics, estrogens);
familial pancreatitis;
Structural abnormalities of the pancreas or duodenum;
infections;
Severe abdominal injury;
Vascular pathology;
Gestational hypertension;
Alcoholism.
Predisposing moments to the occurrence of acute pancreatitis in pregnant women:
Stasis of bile and atony of the gallbladder due to the action of progesterone;
Some increase in the level of enzymes (amylase, lipase, acid protaminase) in the second half of pregnancy as a result of activation of the pancreas;
Increasing the content of lipids in the blood;
Increased intra-abdominal pressure in the second half of pregnancy, leading to increased intraduodenal pressure and intraductal stasis in the Wirsung duct and bile ducts;
The identity of the mechanism that causes contractions of the smooth muscles of the uterus and spasm of the sphincters of the ducts that excrete bile and pancreatic juice;
Constantly available metabolic background due to violations of mineral metabolism, especially with preeclampsia.
Clinical symptoms
Severe pain in the epigastrium, encircling, acute or gradually increasing;
Nausea, vomiting;
Subfebrile condition, tachycardia;
orthostatic hypotension;
Muscle tension.
Laboratory data
When determining diastase (amylase) of serum, it is several times higher than the upper limit of the norm, however, after 48-72 hours from the onset of the acute process, it can return to normal values, despite the ongoing clinic of pancreatitis; amylase levels do not correlate with disease severity. An increase in serum lipase is usually diagnosed.
Traditional methods of examination of the pancreas (pancreatic sounding, angiography, retrograde pancreatography)
fiya) in pregnant women are not applicable. The only possible instrumental diagnostic method that should be used for suspected pancreatitis is ultrasound. The method allows to identify complications of pancreatitis - fluid in the abdominal cavity, abscess, peripancreatic hematoma, formation of pseudocysts; to diagnose cholelithiasis and differentiate it from other surgical pathologies. At a gestational age of up to 30 weeks, ultrasound of the gland does not present technical difficulties, however, at a later date, the uterus may interfere with its visualization; only the body of the gland remains accessible for inspection.
Differential Diagnosis:
Toxicosis of the first half of pregnancy;
preeclampsia;
An interrupted ectopic pregnancy (often with an increase in serum amylase levels);
Perforation of a stomach ulcer;
Acute cholecystitis;
Rupture of the spleen;
liver abscess;
Perinephric abscess.
Complications
Although pregnant women may experience the usual complications of pancreatitis, there is no increased predisposition to them during pregnancy. Acute complications include hemorrhagic pancreatitis with severe hypotension and hypocalcemia, respiratory distress syndrome, pancreatic ascites, abscess formation, and liponecrosis.
Acute pancreatitis in a pregnant woman leads to fetal hypoxia due to transplacental transfer of pancreatic enzymes, hypocalcemia, and maternal fluid and electrolyte disturbances.
Basic principles of treatment
Conservative therapy
1. Infusion therapy.
2. Cessation of enteral nutrition.
3. Nasogastric tube to remove gastric contents.
4. Analgesics, antispasmodics parenterally.
5. Parenteral nutrition (should be started as early as possible to normalize the condition of the fetus).
6. Enzyme inhibitors (trasylol, contrykal).
7. Antibacterial therapy (indicated for pancreatic necrosis).
8. If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy, it is not prolonged.
About 90% of patients respond well to this treatment, before the resolution of the disease takes 3-5 days. Surgical intervention is indicated for peripancreatic abscess, pseudocyst rupture, hemorrhagic and secondary pancreatitis (with cholelithiasis and the development of obstructive jaundice). The tactics are the same as for non-pregnant women.
Surgery
1. Termination of pregnancy for up to 12 weeks.
2. After 36 weeks - early delivery through the birth canal.
3. Surgical intervention is indicated for purulent-septic complications.
4. In the III trimester, in the presence of pancreatogenic peritonitis, a caesarean section is performed, followed by removal of the uterus with tubes and wide drainage of the abdominal cavity.
Convincing evidence of a beneficial effect of abortion on the course and outcome of acute pancreatitis is not available.
Forecast
Prior to the development of medical and surgical management of pancreatitis, the maternal mortality rate was very high at 37%. Currently, maternal mortality is estimated at 3.4%, fetal losses - at 11%.
Acute intestinal obstruction
The increase in the number of operations on the abdominal cavity and inflammatory diseases of the genitals naturally increased the number of severe complications of adhesive disease during pregnancy. The frequency averages 1-3 cases per 10 thousand pregnancies, varies from 1 in 1500 to 1 in 66 500.
Types of intestinal obstruction
 The reasons:
The reasons:
Compression by the growing uterus of intestinal adhesions after previous surgical interventions (60-70%);
Volvulus;
hernias;
Neoplasms.
In the presence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity, there are three critical periods during pregnancy, in which the risk of developing acute intestinal obstruction increases:
The exit of the uterus from the pelvic cavity (3-4 months of pregnancy);
Lowering the fetal head into the small pelvis in the third trimester of pregnancy;
Sudden decrease in the volume of the uterus after childbirth with a rapid change in intra-abdominal pressure.
During these periods, prerequisites are created for a change in the topographic relationships of the abdominal organs. The movement of intestinal loops in the presence of adhesions leads in some cases to kinks, compression, infringement, twisting. A predisposition to the occurrence of acute intestinal obstruction is observed in persons who have undergone ap-
penectomy or female genital surgery. Women are at high risk for intestinal obstruction during their first pregnancy after surgery.
Causes of intestinal obstruction during pregnancy and the postpartum period
Spikes - 55%:
I trimester - 7%;
II trimester - 27%;
III trimester - 45%; Postpartum period - 21%. Volvulus - 25%.
Obstruction of the middle sections of the small intestine - 11%.
Obstruction of the caecum - 36%.
Obstruction of the sigmoid colon - 43%.
Obstruction of other departments - 10%.
Invagination - 5%.
Hernia, carcinoma, appendicitis - 5%.
Other reasons - 10%.
Clinic
On fig. 115 shows the symptoms of intestinal obstruction.
 Rice. 115. Symptoms and diagnosis of intestinal obstruction
Rice. 115. Symptoms and diagnosis of intestinal obstruction
The pain is constant, diffuse, or intermittent, every 4-5 minutes for small bowel obstruction and every 10-15 minutes for large bowel obstruction. With small bowel obstruction, the pain syndrome is more pronounced than with intestinal volvulus and intussusception. Examination of intestinal peristalsis is of little help in establishing an early diagnosis of obstruction; at the onset of the disease, tension in the abdominal muscles is also weakly expressed. Small bowel obstruction usually causes vomiting. In the later stages of the disease, fever, oliguria, shock due to massive fluid loss, acidosis, and infection develop.
If acute intestinal obstruction is suspected in pregnant women with an indication of a history of surgical intervention, an X-ray examination should not be postponed, because the risk of severe consequences of undiagnosed intestinal obstruction far exceeds the risk of an X-ray examination for the fetus. At the onset of the disease, in about 50% of cases, the x-ray is not informative, then a second x-ray is taken after 4-6 hours. Cloiber bowls obviously indicate intestinal obstruction.
Volvulus is the second most common cause of intestinal obstruction during pregnancy (about 25% of cases). Primary obstruction usually occurs in the caecum due to violations of its fixation in the right lateral canal. On the radiograph, the caecum is overstretched and comes into the shadow of the kidneys.
Intussusception is an uncommon cause of ileus in pregnancy and is difficult to diagnose because the obstruction may be transient and typical radiographic findings may be absent.
Treatment
How to carry out conservative therapy is shown in Fig. 116.
After establishing the diagnosis - only surgical treatment (Fig. 117), stabilization of basic vital functions, hydration. The incision is a median laparotomy. The surgical principles are the same as for non-pregnant women. In the event that in the third trimester a large uterus makes it difficult to access the intestines, a caesarean section is performed first.
Forecast
Maternal mortality rate - 10-20% due to late diagnosis and surgery, inadequate preoperative preparation,
 Rice. 116. Explanations in the text
Rice. 116. Explanations in the text
 Rice. 117. Surgical treatment of intestinal obstruction
Rice. 117. Surgical treatment of intestinal obstruction
infection, cardiovascular failure and irreversible shock. Perinatal mortality is even higher (26%), its causes are maternal hypotension, fetal hypoxia.
Stomach ulcer
In pregnancy, there is a protective, apparently estrogen-mediated, effect on gastrointestinal ulcers, so they are rare, although the exact frequency is unknown.
During pregnancy, gastric motility, gastric secretion decreases, and mucus secretion increases.
Signs of peptic ulcer during pregnancy can be mistakenly regarded as signs of pregnancy itself (dyspepsia, epigastric discomfort). With perforation of the ulcer, pain occurs, peritoneal symptoms appear, the clinical picture of shock. Gastroscopy is indicated for diagnosis.
Less than 100 cases of complications of peptic ulcer during pregnancy have been reported in the literature: perforation, bleeding, obstruction, (mostly in the third trimester). The high mortality rate is due to the difficulties of diagnosis during pregnancy. For perforation and bleeding, treatment is surgical; for obstruction, conservative methods are acceptable. In the III trimester, a caesarean section is shown simultaneously to reduce the harmful effects on the fetus of hypotension and maternal hypoxemia.
Spontaneous rupture of the liver and spleen
Spontaneous intra-abdominal bleeding during pregnancy has various causes, including trauma, previous pathology of the spleen, preeclampsia-eclampsia. The exact cause is often unknown. It occurs relatively rarely. The frequency of liver rupture is 1 in 45 thousand pregnancies. Occurs mainly due to preeclampsia, eclampsia, although spontaneous rupture is also possible.
The clinical picture of liver rupture is characterized by abdominal pain, shock, DIC with thrombocytopenia, and a decrease in fibrinogen levels. In typical cases, the hematoma is localized on the diaphragmatic surface of the right lobe, but there may be intrahepatic hematomas. Ultrasound and computed tomography are used to confirm the diagnosis.
With large ruptures of the liver, immediate laparotomy is indicated, ligation of the hepatic artery, resection of the lobe of the liver, suturing of the rupture of the liver, tamponade are possible; infusion therapy, treatment of DIC. The surgical technique and the experience of the surgeon are very important for the survival of the patient.
A ruptured spleen is almost always the result of a traumatic stroke in the distant or recent past (usually with trauma to the chest or abdomen). True spontaneous rupture (not obvious trauma) usually occurs in the second half of pregnancy and reflects the effect of weakening of the splenic stroma from long-standing unnoticed trauma. Such patients may have hemorrhagic shock, clinic
"acute abdomen". Surgical treatment. Maternal mortality is about 15%, fetal death is about 70%.
Rupture of an aneurysm of the splenic artery
According to autopsy data, the frequency of this pathology in adults is 0.1%, in old age it is 100 times more. In 6-10% of cases, there is a rupture of the defect. 25-40% of ruptures occur during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester. Maternal mortality in this pathology is 75% (as well as perinatal), mainly due to incorrect diagnosis and late treatment. Rupture usually occurs late in pregnancy in elderly pregnant women and is associated with splenic atherosclerosis, portal hypertension, and Ehler-Danlos type 4 disease. Often referred to as uterine rupture or placental abruption.
Until the aneurysm ruptures, symptoms are either completely absent or intermittent, the most common manifestation being intermittent pain in the epigastrium or left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It is important to pay attention to the induction of pain in the epigastrium during bending and bending. Although splenomegaly is present, the mass is usually not detected, especially in late pregnancy. A murmur may be heard on auscultation. The diagnosis is reliable when visualized on the radiograph in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen of an oval calcified mass with a central echo-negative area. In a stable clinical situation, angiography is used to establish the diagnosis.
If disease is suspected, immediate laparotomy (in collaboration with the surgeon) is needed to improve maternal and fetal outcomes. The splenic artery is ligated and the aneurysm is resected, the spleen can be left in the presence of collateral blood flow, but in most cases splenectomy is performed.
Pathology of the pelvic organs
Ovarian cysts and tumors during pregnancy are the second most common complication after acute appendicitis when considered together with abdominal and pelvic pathology. Ovarian masses are usually asymptomatic, occurring in 0.1% of all pregnant women. Only in 2% of cases there is a rupture of these formations, torsion - much more often (in 50-60%).
A particularly common ovarian formation in early pregnancy is the gestational corpus luteum, which rarely exceeds 6 cm in diameter. The most common pathological ovarian neoplasms are mature teratomas (21%), serous cystadenomas (21%), corpus luteum cysts (18%) and mucinous cystadenomas.
With ultrasound, the size and consistency of the formation are determined. With a unilateral mobile cystic formation without inclusions, surgery may be delayed until the second trimester.
Differential Diagnosis:
Neoplasms of the intestine;
Myoma node on the leg;
Pelvic kidney;
Congenital anomalies of the uterus.
Indications for surgery during pregnancy:
The mass persists after 15 weeks and is >6 cm in diameter;
Education contains a solid component or partitions;
Education contains internal growths;
There is ascites.
Asymptomatic ovarian masses, first diagnosed in the third trimester, are usually operated on after delivery.
Solid ovarian tumors require surgical treatment during pregnancy due to a possible 2-5% incidence of ovarian cancer and to prevent torsion, rupture, or mechanical obstruction in labor. Solid or cystic ovarian masses detected in the first trimester are surgically removed in the second trimester.
Torsion of the tumor pedicle of the ovary, fallopian tube, and broad ligament can lead to an "acute abdomen" with peritonitis and shock. In this case, other causes are usually assumed and the diagnosis of torsion is made at surgery.
Emergency surgical treatment is indicated. The right ovary is more often involved in the process than the left. The pain is at first gradual, intermittent, then intensifies. Torsion occurs more often in the second trimester. Histologically, these are more often mature teratomas and cystadenomas.
ovarian cancer
2-5% of all ovarian tumors during pregnancy are malignant (dysgerminoma, immature teratoma, serous cystadenocarcinoma).
The tactics of treatment does not differ from that in non-pregnant women - surgery with resection of the greater omentum. Regardless of the gestational age, ovarian cancer is usually treated actively, with the extirpation of all pelvic reproductive organs, the patient should be warned about the possibility of such an operation in advance.
uterine fibroids
Frequency - 0.3-2.6% of all pregnancies. Complications during pregnancy:
malnutrition;
torsion;
Mechanical obstruction in childbirth.
Malnutrition of the node and torsion of the node's leg are accompanied by a clinic of acute abdominal pain and local muscle tension. Conservative therapy is usually carried out, in the presence of torsion of an isolated node on the leg and obstruction in childbirth, surgical treatment is indicated. Myomectomy during pregnancy is not recommended due to the possibility of severe bleeding. With necrosis of the node, the development of DIC is possible, control of the coagulogram is needed.
Initially, the pain is acute, localized, and gastrointestinal symptoms are minimal or absent. The level of smooth muscle enzymes - ACT, LDH, CPK can be increased. With ultrasound, the localization of the node, size, consistency, and the presence of cavities are determined. In early pregnancy, diagnostic laparoscopy is acceptable to differentiate fibroids from ovarian tumors if ultrasound is not informative enough.
Malnutrition of the myomatous node, as a rule, occurs with the phenomena of a threat of termination of pregnancy (increased uterine tone). With timely diagnosis, adequate conservative therapy (antispasmodics, tocolytics) normalizes blood flow in the fibroid node and preserves pregnancy without surgical intervention. When the fetus reaches viability, the decision on the method of delivery and myomectomy is made individually for each patient.
While waiting for the birth of a child, the future father and mother first of all want him to be distinguished by good health. For many couples, the gender of the unborn child is an equally important issue. Knowing that the pregnancy of a boy and a girl differ and what are the signs and signs, the expectant mother can find out the sex already for a period of several weeks.
Very curious parents have the opportunity to find out whether it will be a boy or a girl for a period of 13 weeks based on the results of an analysis of amniotic fluid. But only the second ultrasound examination for a period of 20 weeks can give the most accurate answer. However, many pregnant women do not want to wait for the results of the ultrasound and try to establish whether the son is in the stomach or the daughter by other methods. From this article, you will learn how to recognize the sex of an unborn baby for a period of several weeks: what parameters and features you should pay attention to, and what differences are characteristic of the period of bearing a boy and a girl.
External signs that distinguish pregnancy between a boy and a girl
Already at an early date of several weeks, a woman begins to change, especially externally. According to experts and women in labor, this feature can be used to distinguish between a boy in the stomach or a girl. What factors may indicate that there will be a daughter?
- There are changes in the outlines of the face associated with swelling in the nose and its increase in size, the appearance of a second chin, swelling of the eyelids. As a result, the face loses its former shape and becomes blurry;
- Due to the fact that the hormonal background is changing, from the early weeks of pregnancy, the face becomes covered with pigmentation. This kind of rash can affect any part of the body;
- There are problems with the skin, manifested in the face and body in the form of dryness and various kinds of rashes (pimples, blackheads);
- Due to the lack of calcium and fluorine, leaving mother to daughter, the condition of hair and nails changes - they become brittle;
- There is a change in the shape of the body of the expectant mother, associated with weight gain. This will be evidenced not only by a growing belly, but also by more voluminous hips, buttocks, as well as an enlarged chest. The birth of a girl should be expected if both breasts have significant differences in size, namely the right one is smaller than the left;
- Due to the transfer of a greater proportion of vitamins and nutrients from mother to daughter, female beauty fades for a while.
What changes in appearance occur in expectant mothers of sons and do they differ from external changes during pregnancy with a girl? Women who are carrying boys do not have to face the problem of withering natural attractiveness. On the contrary, during the period of bearing a male fetus, the expectant mother blossoms outwardly, she becomes brighter and more noticeable.
Also, as with a girl pregnancy, there are changes in the physique associated with weight gain.However, if there is a boy in the stomach, then the main difference will be the uniform distribution of the fat layer throughout the body. Outwardly, the figure will remain attractive: the forms will be proportional and seductively rounded.
Other external signs that give out the presence of a male fetus in the abdomen include: a change in the size of the nose, which acquires a pointed and at the same time neat appearance and increased hair growth. Particular hair growth is observed on the legs and abdomen. The reason for this is the male hormone, which rises during the period of pregnancy by a boy. After the birth of a son, the level of hair growth will be the same.
How to distinguish a pregnancy between a boy and a girl by internal sensations

So, we have considered external distinguishing features. However, they are not enough for a complete picture and accurate setting of the sex of the unborn child. It is also worth taking into account some internal and emotional features that suggest for a period of several weeks, whose birth to expect.
To make sure that there will be a girl, you should pay attention to a number of signs. Firstly, women carrying a female child suffer from excruciating toxicosis from an early period and throughout the entire 40 weeks of pregnancy. At the same time, a vivid manifestation of toxicosis is observed not only in the morning, but also in the daytime with the evening.
Secondly, the presence in the girl's stomach will be indicated by urine changed in color, which has become pale yellow or transparent.
Thirdly, expectant mothers of daughters throughout the entire period of pregnancy are accompanied by increased emotionality, capriciousness and pickiness to food. Taste preferences change towards fruits, vegetables and sweets. Women who carry girls are primarily drawn to fruit juices, chocolate and other goodies, such as sweet pastries, sweets. In anticipation of a daughter, expectant mothers prefer to exclude all meat, salty and fish from their products. However, some mothers are sometimes drawn to eat a sweet dessert first, and then something salty, like pickled vegetables. From fruits they prefer persimmons, peaches and watermelons. You can also talk about female gender if the expectant mother is drawn to sour dairy products, such as fermented baked milk and kefir. An important difference is that women who are carrying girls are much less likely to want to eat, compared to women who are expecting boys.
Fourthly, the period of pregnancy for a girl is accompanied by an increased heart rate (up to 150 beats / min), and sometimes the pulse rate reaches 170 beats / min.
These signs are a great helper for every young couple who wants to make sure at an early date that there will be a girl. However, with the help of internal sensations, it is impossible to get a 100 percent result. It is realistic to establish gender with maximum accuracy by means of an ultrasound examination for a period not earlier than 20 weeks.
In the process of bearing a boy, a number of cardinal changes are also observed. What kind of internal sensations distinguish the presence of a male gender in the baby's stomach? Unlike expectant mothers of daughters, they rarely suffer from morning sickness and other manifestations of toxicosis. The next sign that there will be a son is a change in the color of the urine, which takes on a bright yellow hue.
Another difference between pregnancy by a boy is the increased feeling of hunger of the expectant mother. As the weeks of pregnancy increase, women who are carrying sons become more and more hungry.Most often they prefer something meaty or salty. Some are drawn to fried, others to boiled.
The more and more often something meat is used, the higher the likelihood that a boy will be born, since during pregnancy a girl is not drawn to meat at all.
As for fruits, berries and vegetables, future mothers of sons prefer cranberries, tomatoes and lemons.Often, pregnant boys are strongly drawn to another type of vegetable - potatoes, both fried and boiled. A boy should be expected if the expectant mother is drawn to salty.
They prefer pickled cucumbers and tomatoes. Also, many women who are carrying a male child prefer salty not only in the form of vegetables, but also in the form of juices. It also happens that the future mother of her son is drawn to various alcoholic beverages. But sour dairy products do not pull at all.
The fact that there is a boy in the stomach may indicate a mild pregnancy. The results of the analysis of external and internal parameters will help to reassure curious parents who want to quickly find out whether there will be a son or daughter.
Signs of difference in pregnancy between a boy and a girl on ultrasound

Not every pregnant woman trusts her inner intuition and will rely only on sensations and signs.You can more accurately determine the gender of the unborn child by passing certain tests and undergoing examinations. Reliable results are obtained by an ultrasound examination, during which the expectant mother can learn not only about the gender of her child, but also about the presence or absence of any developmental abnormalities.

According to experienced specialists, pregnancy by a boy and a girl during ultrasound diagnostics for a period of several weeks is distinguished by only one parameter - the angle connecting the genital tubercles and the dorsal region of the fetus. Setting the gender of the future baby for a period of several weeks by means of ultrasound diagnostics requires considerable effort, since the development of the genital organs occurs later.

Finding out exactly who is in the stomach - a boy or a girl - is more likely for those women whose gestational age is over 25 weeks. By this period, the formation of the baby is coming to an end, which means that the distinctive sexual characteristics are more clearly visible. Also, for a period of 25 weeks or more, with the help of ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor has the opportunity to say with accuracy whether the development of the baby meets the standards or whether there are violations.

Are there any differences in the shape of the abdomen during pregnancy with a boy and a girl

To determine whether there will be a son or a daughter, many mothers recommend paying attention to the shape of the abdomen. The result of long-term observations of ladies in position was the following conclusions:
- If there is a girl in the stomach, then its shape will resemble a melon. The more weeks, the more vague the belly becomes. Due to the shape in the form of a melon and constant growth, the stomach gradually begins to lose its clear outline. All this makes the waist inconspicuous;
- If there is a boy in the tummy, then its shape will be pointed and raised to the top. The more weeks, the more noticeable the growth of the abdomen along with the protruding and upturned navel.
Young mothers who diagnose the sex of the unborn baby on such grounds as the growth and shape of the abdomen should be aware of the existence of an error. This method works effectively only in certain cases: if a woman is pregnant for the first time, her figure has ideal parameters, and there are no deviations from the norm in the size of the fetus. In other cases, the assumption of whether it will be a boy or a girl based on the height and shape of the abdomen may be erroneous. The reason for this may be individual physiological characteristics. To increase the accuracy of the result will help information about what shape of the abdomen when carrying a boy and a girl was in women in the family line. However, in this case, it is not worth starting preparations for the birth of a baby of the established gender. The shape and growth of the abdomen can be influenced by various factors:
- With multiple pregnancies, the abdomen differs significantly in size due to the growth of several babies;
- The fact that a woman is not nulliparous will greatly complicate the determination of the sex of the fetus by such parameters of the abdomen as shape and height. During the first pregnancy, the shape of the abdomen is pointed, and during subsequent births, it may change due to stretching of the abdomen;
- With an excess of amniotic fluid, the abdomen will look larger than it should be for a given number of weeks;
- Under the fullness of the mother, the growth of the abdomen may be hidden;
- If the child has taken a non-standard position in the womb (obliquely or across), then the shape of the abdomen will be changed;
- In women with a narrow pelvis, regardless of the sex of the fetus, the abdomen will be sharp and neat in shape, as well as small in size;
- If there is an increase in the size, weight and growth of the fetus relative to the norm, then the stomach will be larger.
In addition, the shape of the abdomen can change under the influence of muscle tone inherent in the uterus and abdominal wall. It is more difficult for large and tall women to determine the sex of the child by one of the parameters of the abdomen, since its growth is not noticeable for a long time. Expectant mothers of fragile physique and short stature will have a larger belly from the earliest weeks.
All signs and patterns arise on the basis of long-term observations. But in fact, each pregnancy is individual and cannot completely coincide with the pregnancy of other women.Many women in labor claim that during the period of bearing a child of one sex, there were some signs that are characteristic of pregnancy with a child of the opposite sex.
The main distinguishing features of pregnancy for a boy and a girl

In order to simplify the process of determining the gender of an unborn baby, you can use a single list of signs that distinguish between a boy and a girl pregnancy.
So, the presence in the girl's stomach is accompanied by the following features:
- There is a legibility and pickiness in food, the choice is often in favor of fruits, vegetables and sweet desserts. No less than fruits and vegetables, future mothers of daughters prefer sour dairy products;
- There are changes in appearance in the form of a loss of attractiveness;
- Behavior is accompanied by laziness and passivity;
- There are concerns associated with swelling, edema and varicose veins. This especially affects the feet and lower legs;
- In the process of growth, the stomach takes the form of a melon, which makes it blurry;
- There is significant breast growth.
Other factors testify to the presence in the boy's stomach. Firstly, the expectant mother changes outwardly, becoming even more attractive. Secondly, the abdomen becomes sharp and bulging. Thirdly, taste preferences are changing in favor of vegetables such as tomatoes and potatoes. Especially women pregnant with boys prefer salty and meat. They want to eat such dishes more and more. Fourthly, hair growth increases. Especially noticeable is the increase in hair on the legs. And the last difference between a boy's pregnancy is an increase in the size of the nose, associated with a slight swelling.

Do you believe that thoughts are material? Then remember who you imagined at the moment of conception - a boy or a girl? In fact, the gender of the child is not the most important thing, it is much more important that the baby is healthy and happy.
Modern ultrasound diagnostics already at 4-5 months of pregnancy allows you to determine who - a boy or a girl - is in the womb. And in the old days, women could only guess and notice who to expect. A huge number of various signs have come down to our time, according to which our great-great-grandmothers calculated the sex of the unborn baby.
Of course, we all know that not all signs come true. But it is more interesting to live with them; and as for the appearance of the child, then attempts to guess who is sitting there in your tummy, fan the time of pregnancy with special romance. And not all women want to find out the gender of the child during a sound examination, preferring that this be a pleasant surprise for them. Of course, it is impossible to completely abandon ultrasound: it is necessary in order to control the development of the child. But for myself, I decided that when the second pregnancy comes, I will not find out in advance who will be born with us.
So, a lot of signs will be accumulated. Watching your feelings, the shape of the abdomen, the activity of the baby is so funny that most women follow this with pleasure, not even paying attention to the ultrasound readings. In the end, technology is technology, but our feelings are always with us, and we communicate with our child not through the apparatus, but - first of all - at the level of intuition, and not from case to case, but every minute, constantly feeling in ourselves the beat of his life. And, of course, we want to know what certain moments in his behavior or our condition could mean.
In general, the list of signs that I have collected is quite voluminous; and many of them overlap in meaning. Therefore, I tried to choose the most, in my opinion, interesting:
So, about the birth of a boy show the following signs:
- In the first trimester of pregnancy, morning sickness is completely absent.
- Fetal heart rate less than 140 beats per minute.
- The abdomen is low and protrudes forward.
- Belly round like a basketball.
- The areolas around the nipples of the breast are very dark.
- You have become prettier, just flourished.
- Constantly pulls on salty and sour.
- The body requires protein foods: meat, milk or cheese.
- My feet are getting colder.
- Hair grows faster than usual on the legs.
- The skin of the palms is very dry.
- The nose is slightly pointed.
- You have a headache.
- The color of urine has become bright yellow.
- Since the husband and wife are halves of one whole, the pregnancy should also affect the spouse. So, if a man does not lag behind you, strenuously gaining excess weight, expect a boy.
- In the evening, when you and your husband dream of a future child, conduct such an experiment. Remove the wedding ring from your hand and hang it on a string above your stomach. This will be more convenient for your spouse. If the ring begins to spin in a circle, then the child is male, but if you swing from side to side, a girl will be born.
To what a girl will appear, indicate the following signs:
- In the morning, nausea haunts, which lasts the entire first trimester of pregnancy.
- The fetal heart rate reaches 140 beats per minute or even more.
- You will not recognize yourself in the mirror: the figure is blurred in the most "dangerous" places - fat is deposited on the hips and buttocks.
- The mammary glands increase unevenly: the left has become larger than the right.
- Your breasts have grown significantly.
- Your hair has suddenly acquired some kind of reddish tint.
- The girl takes away the beauty, so you have become a little ugly.
- The belly is high and resembles a melon in shape.
- Your culinary habits have changed in such a way that you now prefer sweets and fruits, especially oranges.
- For some reason you began to eat bread without a crust.
- You are capricious, offended over trifles, have become sentimental and suspicious - this is completely natural: after all, 2 women already live in you.
- Despite the creams, the skin of the face is still dry.
- Urine has a dull light yellow tint.
An acute belly during pregnancy, or a belly that has a different shape, indicates that soon a woman can give birth to a child whose gender will correspond to the shape of the tummy in which he is all the time before his birth.
Determining the sex of the child by the shape of the belly of the expectant mother is quite simple. Pregnant women, as well as future fathers, are positive about this way of determining who the family should expect soon. Although ultrasound is an equally effective way to find out who should be expected in the family in the near future, folk methods for determining the sex of an unborn child are also very popular both among pregnant women for whom childbirth will not be the first, and for those expectant mothers who give birth for the first time. .
What does the shape of the abdomen indicate during pregnancy?

The boy is characterized by a neat little low belly during pregnancy. Despite the fact that a woman is pregnant, her rounded belly can only be seen from the front. If you look at the future mother from the back, it is quite difficult to guess that the woman is in an interesting position. A sharp belly indicates that a boy will soon appear in the family, so it’s worth preparing a blue envelope for the mother and child to be discharged from the parental home and decorating the baby’s room with wallpaper with cars.
If the pregnancy ends with the birth of a girl, then the belly looks noticeably different from the previous description, as it looks much larger than those of women who are expecting a boy. For pregnant women expecting the birth of a girl soon, the presence of an oval oblong tummy is characteristic. During pregnancy, the girl's belly increases not only upwards, but also to the sides. Because of this, the waist area of the expectant mother becomes much wider than before. Usually, it is possible to notice that a woman is pregnant only when the expectant mother is waiting for the birth of her daughter.
If a woman does not trust such methods of determining the sex of a child and still wants to do an ultrasound, she may simply not attach any importance to the shape of her abdomen. At the same time, the expectant mother should be prepared for the fact that the people around her will tell her what sex she should expect in the near future, since many people can determine the sex of the baby by the shape of the mother's abdomen.
Doctors believe that it is not possible to predict the sex of a child by the shape of the abdomen. The size of the abdomen and its shape has nothing to do with the sex of the fetus inside. Many different studies have been conducted around the world, on the basis of which doctors have concluded that the shape of the abdomen has nothing to do with the sex of the unborn child. That is why among specialists such a method for determining the sex of a child, as a careful examination of the abdomen of a woman in labor and determining its shape, did not find fans.
 At the same time, it has been proven that the shape of the abdomen can be influenced by the physiological characteristics of each woman in labor individually. If the expectant mother has a narrow pelvis, then the stomach, respectively, protrudes slightly forward during pregnancy. In the event that a pregnant woman has rather wide hips, then the stomach spreads in different directions and looks uneven.
At the same time, it has been proven that the shape of the abdomen can be influenced by the physiological characteristics of each woman in labor individually. If the expectant mother has a narrow pelvis, then the stomach, respectively, protrudes slightly forward during pregnancy. In the event that a pregnant woman has rather wide hips, then the stomach spreads in different directions and looks uneven.
The form may also depend on other factors that become known only at the time of the development and course of pregnancy. For example, the rate of weight gain in a pregnant woman may also have an impact on the fact that the stomach subsequently takes any particular shape. Attention should also be paid to the fact that an excessive amount of fat will not subsequently disappear along with extra kilos, which are formed from the weight of the fetus itself and amniotic fluid. It will be deposited even at the waist of a young mother. And it will not be so easy for a woman to get rid of it compared to how easy it was to gain this weight.
It can be concluded that determining the sex of a child by the shape of the belly of the expectant mother is not as effective as, for example, ultrasound.
However, despite the fact that almost all experts consider this method ineffective, young mothers will still continue to try to determine the sex of their child in this way. It is possible that a coincidence of circumstances will make it right.
Pregnancy: how to determine the sex of the child in other ways
 If a woman observes nausea in herself exclusively in the morning, then most likely she will have a girl. If, however, attacks of nausea haunt a woman throughout the day, it's time for her to buy a blue envelope for discharge from the parental home, because she will soon have a boy.
If a woman observes nausea in herself exclusively in the morning, then most likely she will have a girl. If, however, attacks of nausea haunt a woman throughout the day, it's time for her to buy a blue envelope for discharge from the parental home, because she will soon have a boy.
If the hairline on the legs began to grow noticeably faster, we should expect the birth of a boy. For pregnant women whose leg hair has grown much more slowly, it will certainly be interesting to know that this is due to the birth of a girl soon.
If your nose is slightly swollen during pregnancy, do not be upset when looking at yourself in the mirror. Soon a son will be born to a pregnant woman, and the nose will subsequently become the same as it was before.
Girls love sweets and fruits. And the boys prefer meat and hearty dishes more.
In order to determine the sex of the unborn baby, a woman just needs to observe a little what she most wants to eat. If these are sweets, a beautiful daughter will be born soon.
 If a pregnant woman cannot live a day without eating a piece of fatty meat, she should soon expect the birth of the future favorite of the whole family - a son.
If a pregnant woman cannot live a day without eating a piece of fatty meat, she should soon expect the birth of the future favorite of the whole family - a son.
To determine the sex of the unborn child, a woman in labor should carefully examine her stomach. The belly during pregnancy as a boy, according to folk wisdom, outwardly will be very different and look different than the belly during pregnancy as a girl. If a pregnant woman notices that a few extra hairs have appeared on it, the couple will soon have a boy. A woman who has pigmentation on her stomach during the process of bearing a child should not worry. This is just a clear sign that she will soon have a daughter.
Additional points
From the heartbeat of a pregnant woman, according to popular belief, it also depends on who will be born to her in 9 months. If the heart beats fast, it means that a girl will be born to a young mother. A boy will be born if the heartbeat is slower than it was before pregnancy.
A woman's mood during pregnancy can say a lot. Usually those women who will soon give birth to a girl are not in a good mood. Something bothers them all the time, something irritates them and they don’t like everything.
Unlike capricious girls, boys in their mothers' belly behave calmer and more restrained. A woman in an interesting position is not worried about anything. She does not worry about any reason, she is completely satisfied with her current state.
According to folk signs, without much difficulty it is possible to determine the sex of the child, starting from the side in which the woman first heard the baby move. If this happened on the right side, a boy should be expected. If the movement was on the left side, the woman will soon become the mother of a charming daughter.
If the blow inflicted by the child is located in the region of the liver, it means that a girl will be born to the expectant mother. If the blows constantly fall on the bladder area, it means that the woman will give birth to a boy. Of course, it is quite difficult to determine the sex of the baby in this way, since the blows can be too varied and fall into different places. A woman simply does not have time to remember where each of them falls in order to subsequently make a correct prediction.
BUT. Diagnostics. During pregnancy, the clinical picture of acute diseases of the abdominal cavity changes, which greatly complicates their diagnosis. A detailed study of the anamnesis and laboratory data, as well as a thorough physical examination, help to make the correct diagnosis and decide on the need for hospitalization and emergency surgical intervention. The features of surgical treatment of these diseases during pregnancy will be considered below.
B. Surgery
1.Acute appendicitis. As the size of the uterus increases, the localization of the appendix changes, which leads to a variety of clinical manifestations of acute appendicitis. The risk of gangrenous appendicitis and perforation of the appendix in the III trimester of pregnancy is higher (69%) than in I and II (31%). With perforation, perinatal mortality reaches 28%, and in its absence - only 5%. In this regard, if acute appendicitis cannot be ruled out, emergency surgical intervention is indicated. With timely surgical treatment of acute appendicitis, maternal mortality can be reduced to almost zero, while in 20-25% of cases there is an overdiagnosis of the disease. Since the risk of misdiagnosis is high, in the first trimester of pregnancy, the median laparotomy is considered the most convenient operative approach. In late pregnancy, the incision is made directly over the site of greatest pain. Regardless of whether the appendix is changed or not, it is removed. With peritonitis and appendicular abscess, the abdominal cavity is drained and broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. In rare cases, it is necessary to impose a cecostomy. At full-term pregnancy and diffuse peritonitis, a caesarean section is indicated. With gangrenous appendicitis, if there is a high risk of spreading the inflammatory process to the uterus, it is extirpated. Complications of appendectomy include preterm labor and wound infection, so tocolytic therapy and delayed abdominal sutures are usually needed.
2.Acute cholecystitis- the second most common (after acute appendicitis) surgical disease in pregnant women. Biliary colic attacks requiring cholecystectomy are rare. In 3.5% of pregnant women, gallstones are discovered by chance (during planned ultrasounds). Among women aged 16-45 who underwent cholecystectomy, pregnant women accounted for 0.3%. Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis and gallstone disease in pregnant women is the same as in non-pregnant women. The localization and nature of pain in pregnant women do not change, but local symptoms are usually mild. Acute cholecystitis in pregnant women has to be differentiated from acute appendicitis, peptic ulcer and other surgical diseases. To confirm the diagnosis, ultrasound is now used instead of X-ray and isotope studies.
Acute cholecystitis is initially treated conservatively: aspiration of the contents of the stomach through a nasogastric tube, fluid infusion, analgesics. Indications for surgical intervention are the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, repeated attacks, obstructive jaundice, suspicion of gallbladder perforation, or other complications. If it is possible to postpone the operation, it is better to perform cholecystectomy in the second trimester of pregnancy, since in the first trimester there is a high risk of spontaneous abortion and teratogenic effects of general anesthetics, and in the third trimester the operation is technically more difficult to perform. There are reports of successful laparoscopic cholecystectomy at 13–23 weeks' gestation. In the future, all women had healthy children.
3.Chronic inflammatory bowel disease. With an exacerbation of nonspecific ulcerative colitis, conservative treatment is usually effective. Indications for surgical intervention are fulminant course of the disease, intestinal obstruction, toxic megacolon, not amenable to conservative treatment, massive bleeding, peritonitis, suspicion of colon cancer. In such cases, a subtotal colectomy may be required. Operations of a smaller volume give only a temporary effect. In Crohn's disease, surgical intervention is indicated for the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, intestinal obstruction, abscesses and fistulas. Usually produce resection of the affected area of the intestine and prophylactic appendectomy.
4.Intestinal obstruction in pregnant women, it can be caused by adhesions, volvulus, intussusception, and strangulated hernia (in descending order of frequency). Requires urgent surgery. Preoperative preparation (aspiration of the contents of the stomach through a nasogastric tube and treatment of metabolic disorders) should take as little time as possible. After restoration of intestinal patency, a thorough revision of the abdominal organs is performed.
5.Liver rupture is rare and almost always associated with preeclampsia or eclampsia. With surgical treatment, maternal mortality is 33%, with conservative treatment - 60-96%. Conservative treatment is permissible only with subcapsular hematoma of the liver. Rupture of the liver with intra-abdominal bleeding is an indication for emergency surgical intervention. The damaged vessels are tied up, the liver tissue is sutured with atraumatic needles. Electrocoagulation and hemostatic sponges are used to stop bleeding. Selective embolization of bleeding vessels is also effective. To save the baby, eliminate preeclampsia and provide prompt access, a caesarean section is usually performed.